



MOBILEcharge
Smart charge management
Peak shaving
Reduce costs
Less CO2 emissions
per e-bus with green electricity p.a.
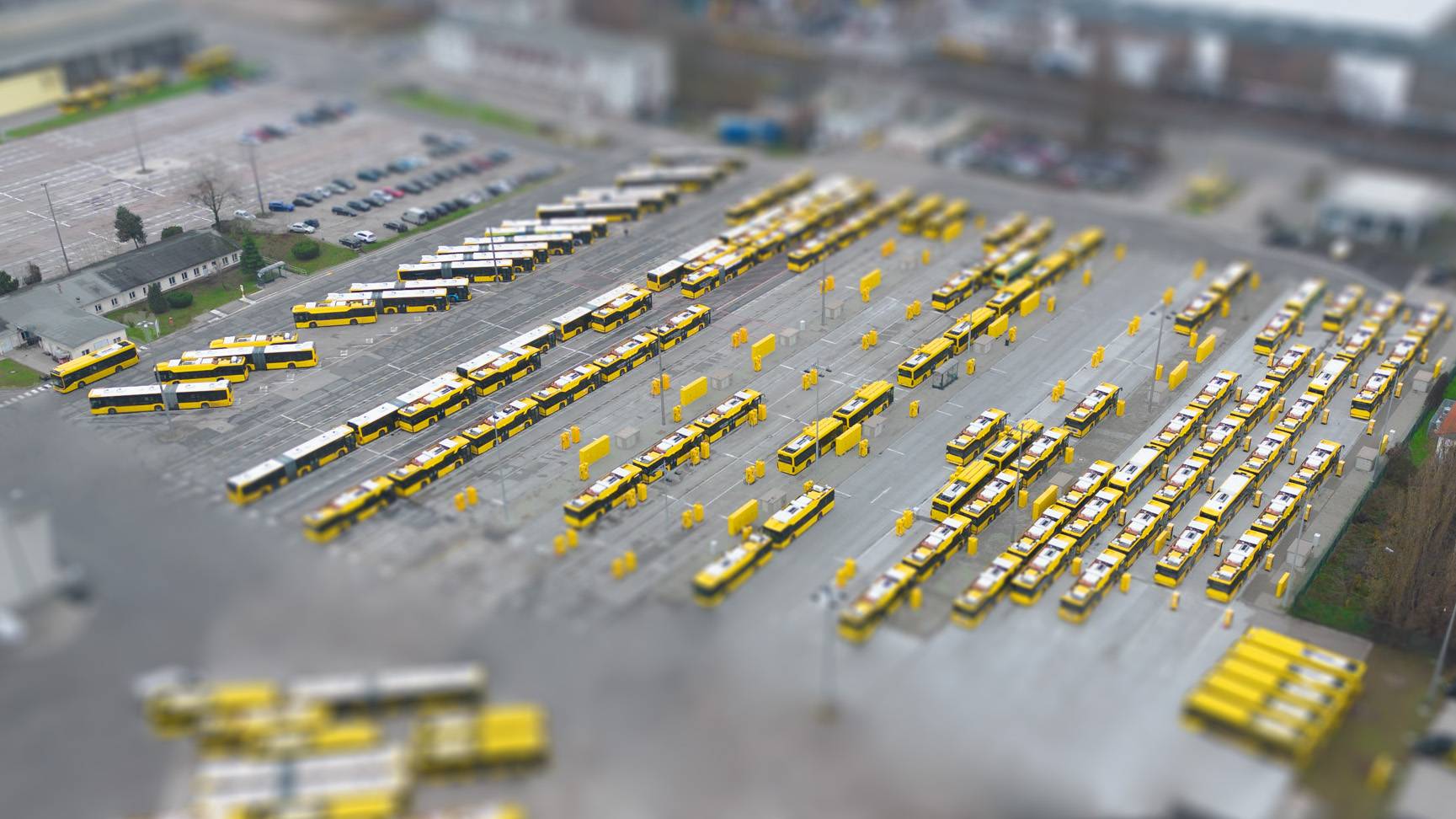
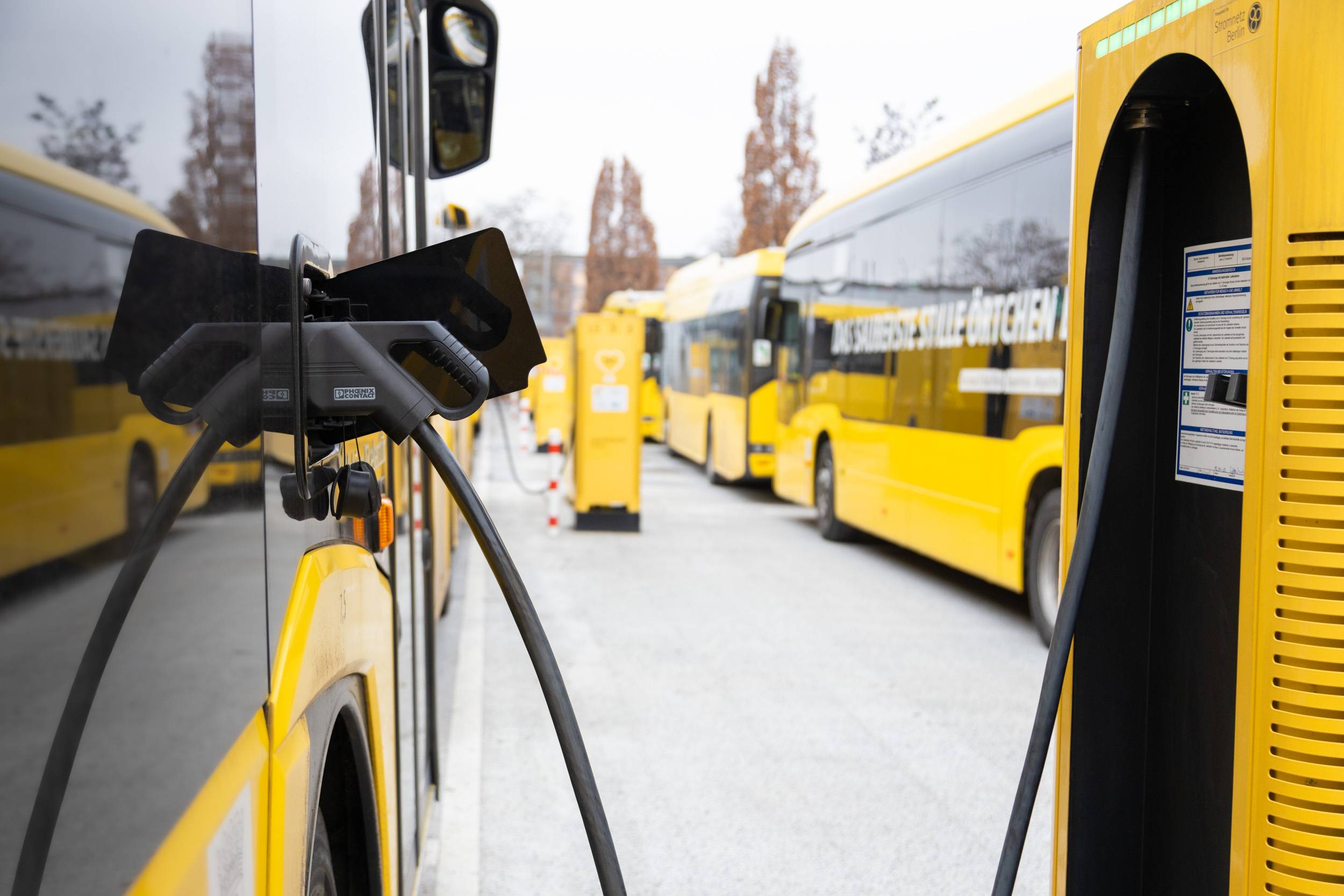
Intelligent charging of e-buses
This is how smart charge management works. Constant communication can ensure that your e-bus fleet is charged on demand, cost-effectively, and with minimum impact on the battery
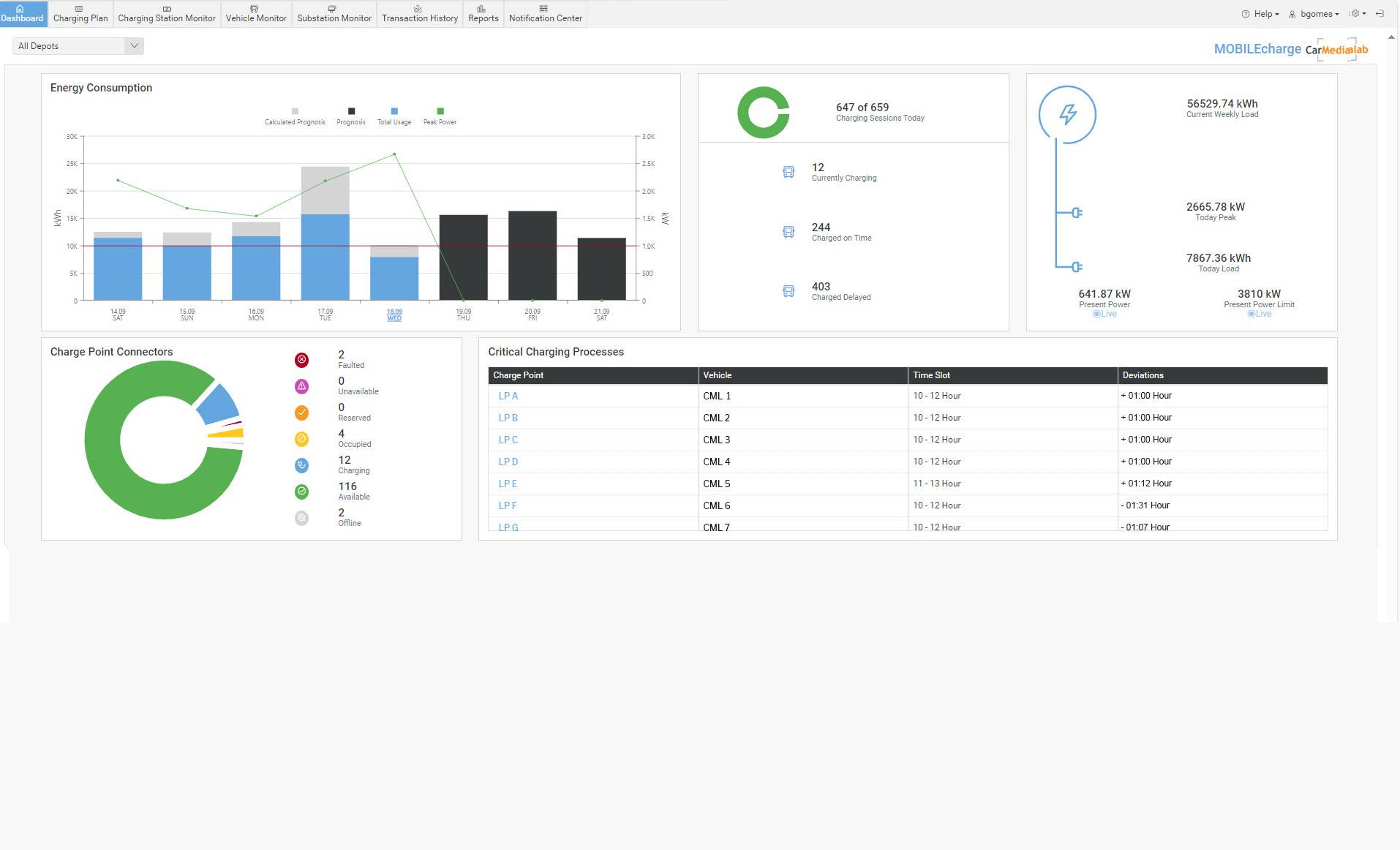
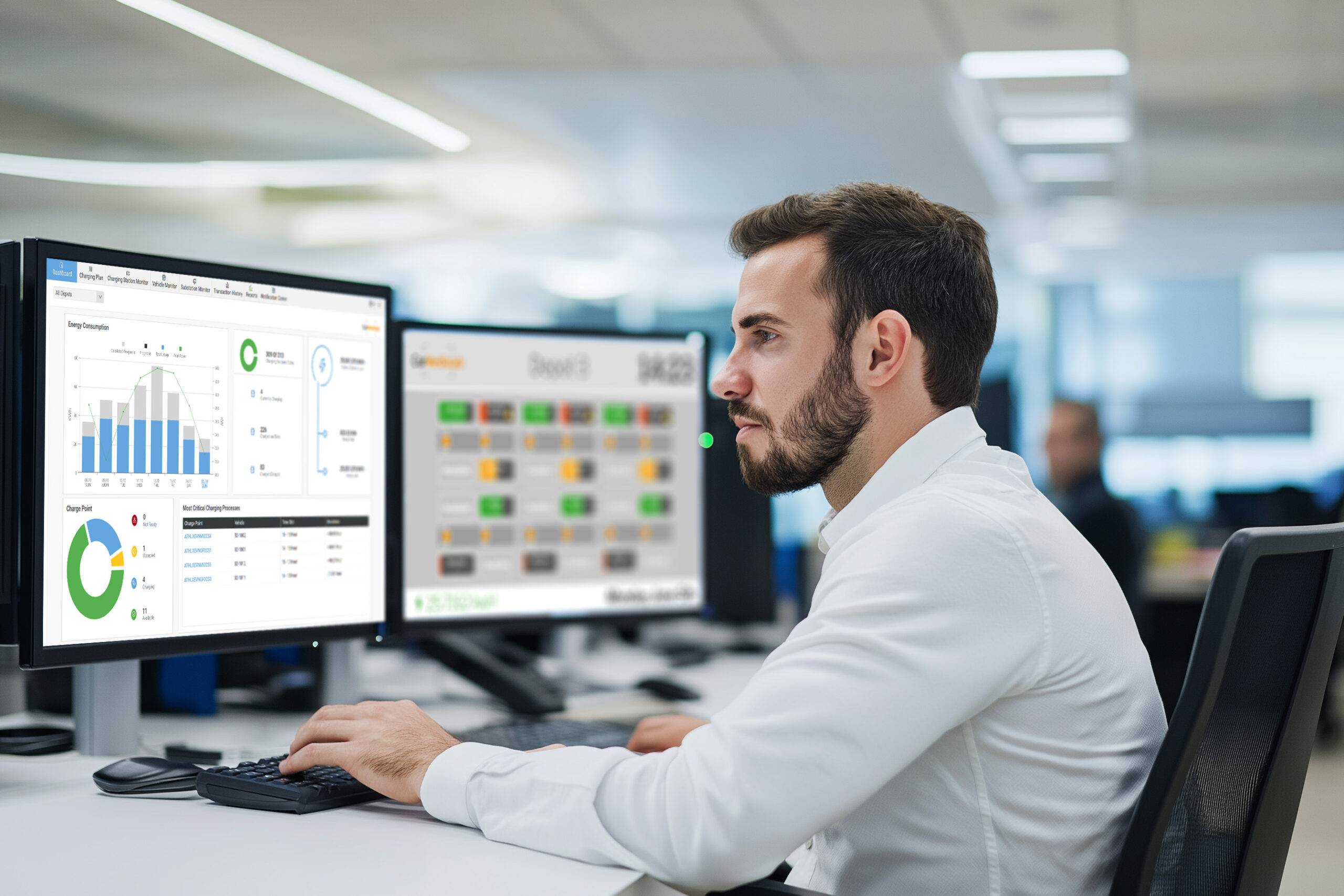
Dashboard
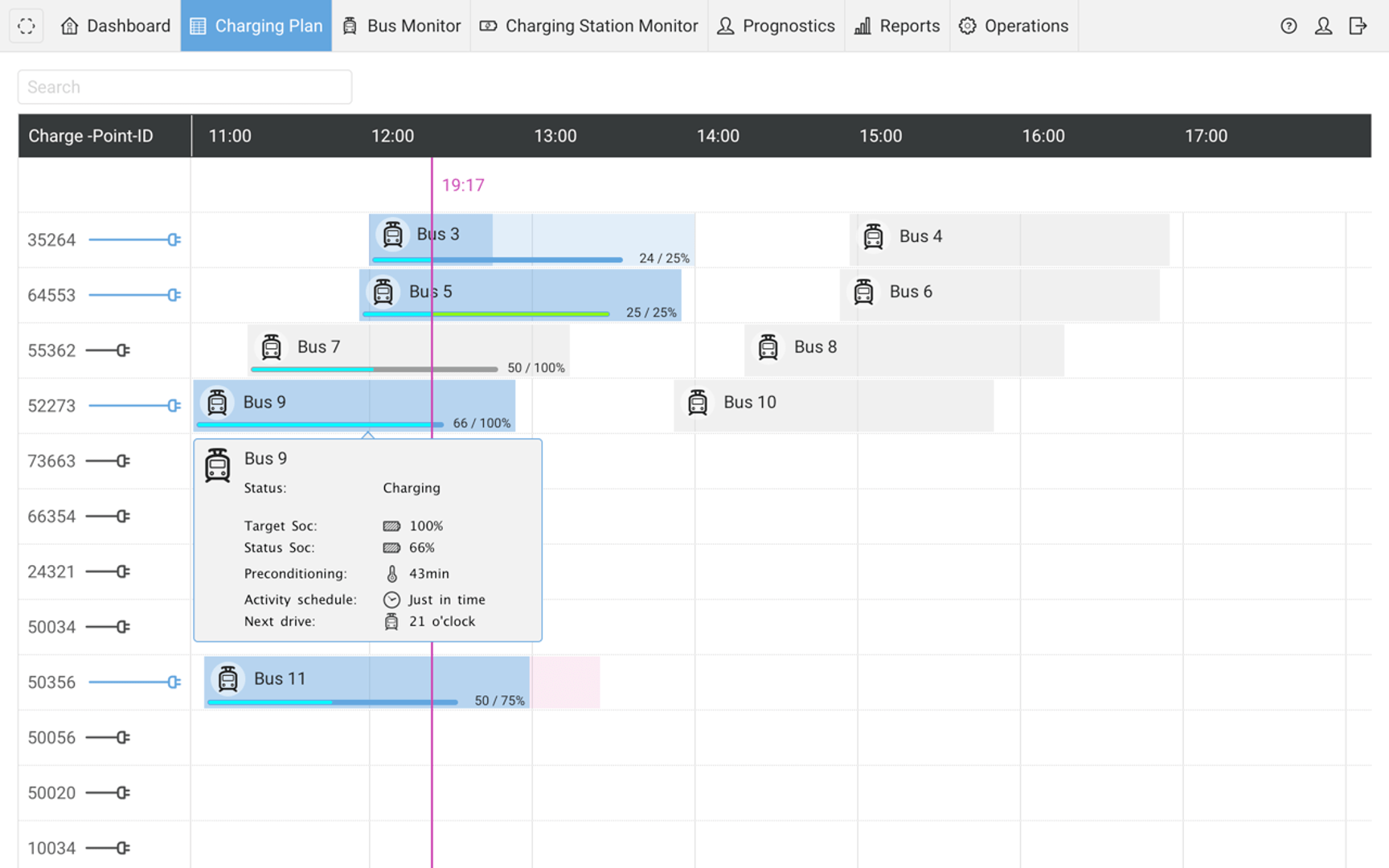
Charging plan
Keep an eye on your depot
Explained in 30 seconds
Key features at a glance
The solution for complex operations
Overview of MOBILEcharge Plans
Core
Key features
- Load management
- Charging station monitoring
- Remote maintenance with OCPP 1.6 or 2.0.1
- Vehicle monitoring
- Reports & real-time notifications
Most popular
Smart
Core-Plan +
- Advanced charging strategies
- Charging according to schedule with VDV 463
- Preconditioning with VDV 261
- Customer-specific interfaces
- Export of all historical charging data
Power
Smart-Plan +
- Charging strategies based on battery condition & electricity price
- Integration of substations
- Integration of renewable energies
- Integration of vehicle data
- Customer-specific reports
The solution for complex operations
Powerful Tools
How your company benefits from MOBILEcharge
The best smart charging solution
Intelligent charging processes
Centralized charge management
Optimized charging performance
Battery saving
Standards
Control
Active diagnostics and remote control of charging points and transformers.
Independent and safe data
Valuable insights & actionable advice
Easy to integrate
More compatibility between manufacturers
Partner of open standards




Satisfied customers worldwide

Eric F.
Sustainability is at the core of who we are as a public transportation provider, and battery-electric buses are crucial to our zero-emission future. We’re excited to partner with CarMedialab to improve the performance of these vehicles, and the experience for our riders.

Shirley W.
We chose CarMedialabs charge management system for all our bus depots all over Israel. MOBILEcharge will help us to have a maximum number of buses available on time with minimal use of the grid and minimal costs. Let the electrification revolution begin!

Melissa D.

Hugo V.
Wonderful collaboration […] we will look forward to continuing this really good work.

Anton G.

Tore G.
Finally somebody who’s understanding smart charging entirely.

Dennis H.
The long-awaited system for vehicle data testing. We as VCDB have a great interest in the Data Tester, as we also provide vehicle inspections for customers.

Paul G.
It’s been a pleasure working with you guys from the beginning and the best is yet to come!

Mark S.
A great example of how our customers can benefit with their ISO 15118 adaption through partnership and collaboration.





































A selection of our projects

Israel
450 e-busses
1.372 charging points

Senegal
121 e-busses
120 charging points

Spain
83 e-busses
200 charging points

Norway
138 e-busses
100 charging points

USA
40 e-busses
12 charging points
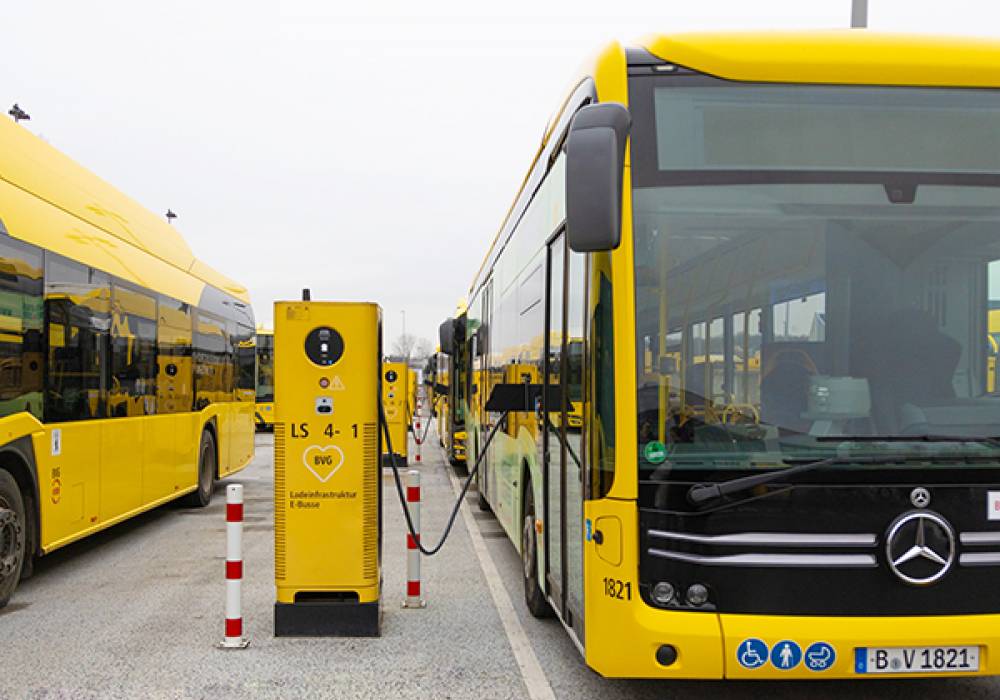

Germany
221 e-busses
56 charging points
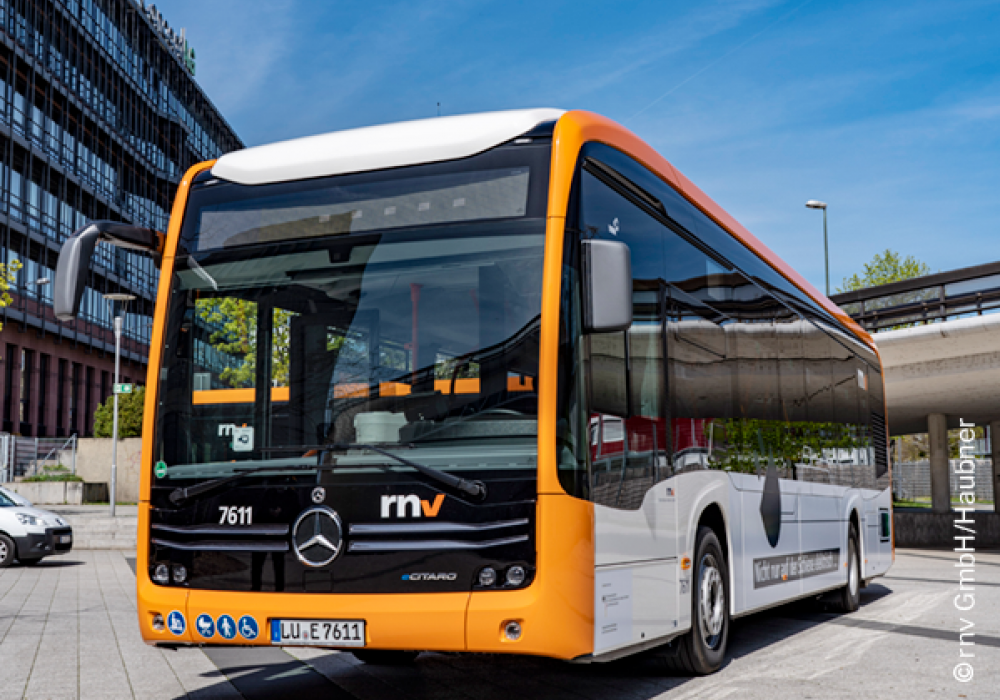

Germany
84 e-busses
62 charging points
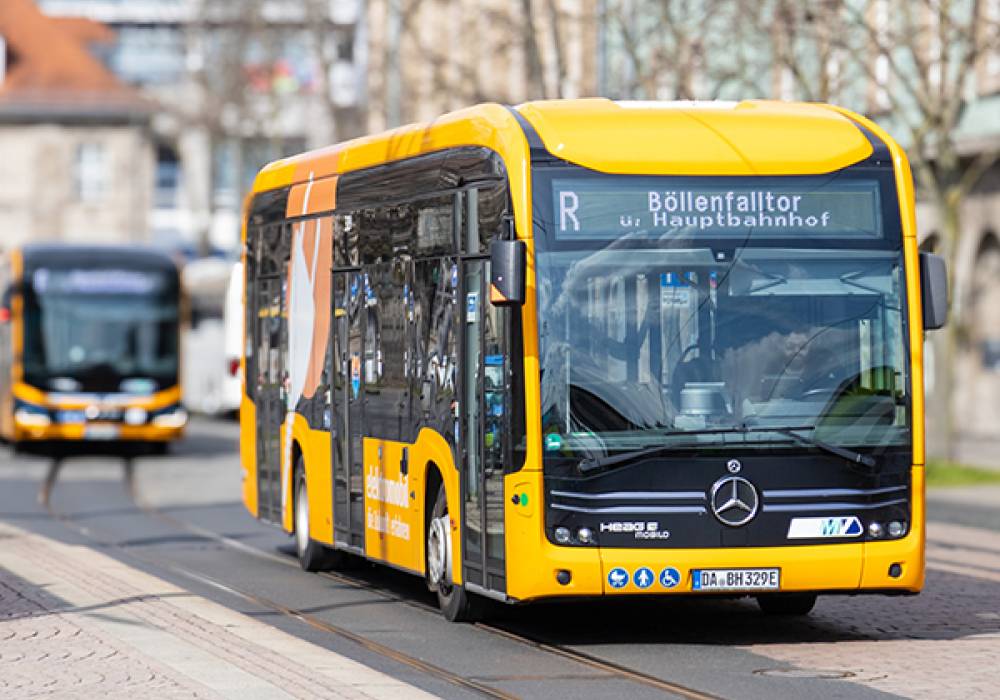

Germany
43 e-busses
48 charging points
Worldwide most advanced technology



Contact me!
All at a glance
You may also be interested in
Public Transport News

Intelligent Energy Distribution Between Metro and E-Bus Fleet in Barcelona

VDV 261 in Practice: Advancing Interoperability with RATP in Paris

CarMedialab delivers charge management for Keolis Netherlands

Experience in the introduction of e-buses

Swiss transport company chooses CML and INIT for a comprehensive solution for operations control and e-mobility
Find more insights about Public Transport
Our blog also gives you regular updates about our products, partnerships and our company in general.





